Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections, affecting millions of people worldwide each year. While they can occur in anyone, women are at a higher risk due to their anatomy. UTIs can range from mild discomfort to severe complications if left untreated. In this deep dive, we’ll explore what UTIs are, their causes, symptoms, complications, treatment options, and prognosis.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
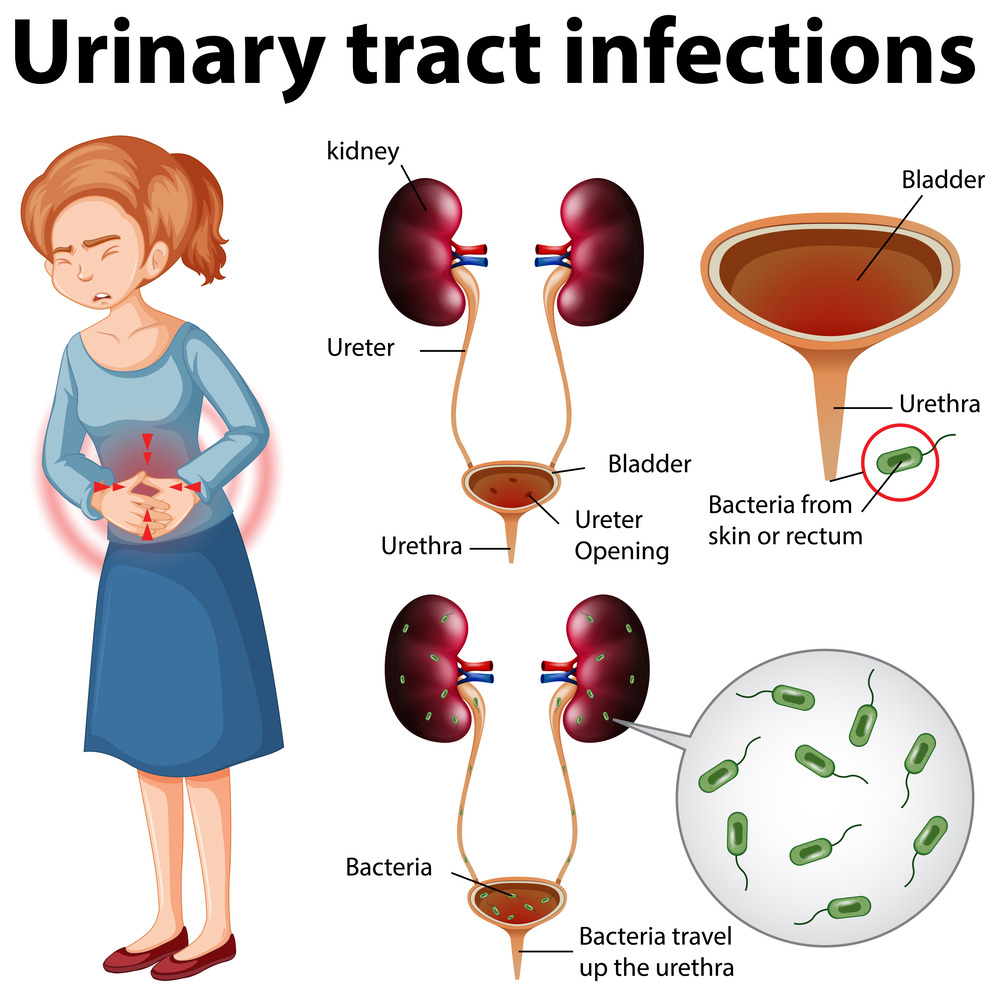
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most UTIs occur in the lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra) and are caused by bacteria, although fungi and viruses can also be responsible in rare cases.
UTIs are classified based on the part of the urinary tract they affect:
- Cystitis: Infection of the bladder.
- Urethritis: Infection of the urethra.
- Pyelonephritis: Infection of the kidneys (a more serious condition).
Causes of UTIs
UTIs are primarily caused by bacteria, with Escherichia coli (E. coli) being the most common culprit. These bacteria typically enter the urinary tract through the urethra and multiply in the bladder. Other causes and risk factors include:
1. Bacterial Entry
- Poor Hygiene: Wiping from back to front can introduce bacteria into the urethra.
- Sexual Activity: Can push bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Catheter Use: Increases the risk of bacterial entry.
2. Anatomical Factors
- Shorter Urethra in Women: Makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
- Enlarged Prostate in Men: Can obstruct urine flow, increasing infection risk.
3. Other Risk Factors
- Weakened Immune System: Makes it harder to fight off infections.
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Congenital or acquired structural issues.
- Menopause: Reduced estrogen levels can increase susceptibility.
- Diabetes: High sugar levels can promote bacterial growth.
Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of a UTI depend on which part of the urinary tract is affected. Common symptoms include:
Lower UTIs (Cystitis and Urethritis)
- Pain or Burning During Urination: A hallmark symptom.
- Frequent Urge to Urinate: Even when the bladder is empty.
- Cloudy or Bloody Urine: May indicate infection.
- Pelvic Pain (in Women): Often felt in the lower abdomen.
- Rectal Pain (in Men): May occur with urethritis.
Upper UTIs (Pyelonephritis)
- Fever and Chills: Indicates a more severe infection.
- Flank or Back Pain: Pain in the kidney area.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Common with kidney infections.
- Fatigue and Malaise: Feeling generally unwell.
Complications of UTIs
If left untreated, UTIs can lead to serious complications, including:
1. Recurrent Infections
- Some individuals experience multiple UTIs within a short period.
2. Kidney Damage
- Untreated pyelonephritis can cause permanent kidney damage or scarring.
3. Sepsis
- A life-threatening condition where the infection spreads to the bloodstream.
4. Pregnancy Complications
- UTIs during pregnancy can increase the risk of preterm birth or low birth weight.
Treatment Options for UTIs
The primary treatment for UTIs is antibiotics, but the approach may vary depending on the severity and location of the infection.
1. Antibiotics
- Lower UTIs: Commonly treated with oral antibiotics like trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, or fosfomycin.
- Upper UTIs: May require stronger antibiotics or intravenous (IV) treatment in severe cases.
2. Pain Relief
- Phenazopyridine: Helps relieve burning and urgency.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
3. Home Remedies
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria.
- Cranberry Juice: May help prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall (evidence is mixed).
- Probiotics: Can support a healthy urinary tract.
4. Preventive Measures
- Good Hygiene: Wipe from front to back and urinate after sexual activity.
- Avoid Irritants: Such as harsh soaps or douches.
- Stay Hydrated: Promotes regular urination and flushes out bacteria.
Prognosis for UTIs
The prognosis for UTIs is generally excellent with prompt treatment. Key points to consider:
1. Quick Recovery
- Most uncomplicated UTIs resolve within a few days of starting antibiotics.
2. Prevention of Recurrence
- Adopting preventive measures can reduce the risk of future infections.
3. Monitoring for Complications
- Severe or recurrent UTIs may require further investigation to rule out underlying issues, such as kidney stones or structural abnormalities.
4. Long-Term Outlook
- With proper management, most individuals can avoid long-term complications and maintain a healthy urinary tract.
Conclusion
Urinary Tract Infections are common but manageable conditions that can cause significant discomfort if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms early, seeking prompt medical attention, and adopting preventive measures are key to avoiding complications and maintaining urinary health.
If you suspect you have a UTI, consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Remember, early intervention is the best way to ensure a quick recovery and prevent recurrence.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights into UTIs. If you have any questions or experiences to share, feel free to leave a comment below. Together, we can build a supportive community for those navigating urinary health. 💧
